Download the ISO image and burn the same onto a USB stick.
Insert the USB stick in the server and power on (My server is Dell R430)
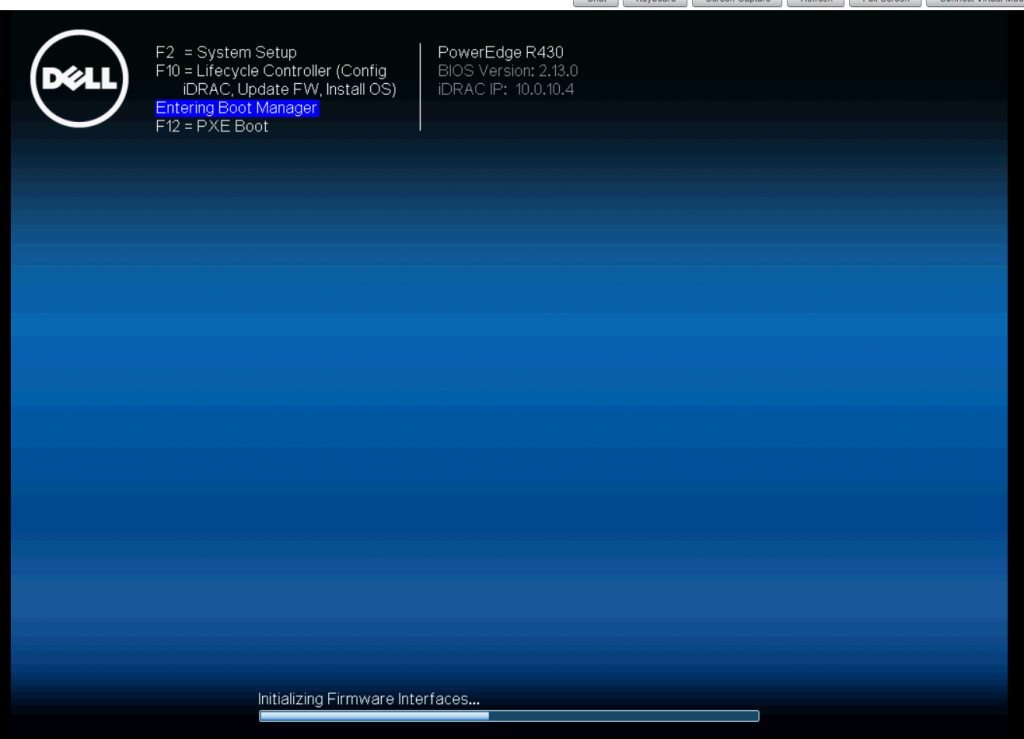
Press F11 and enter Boot Manager
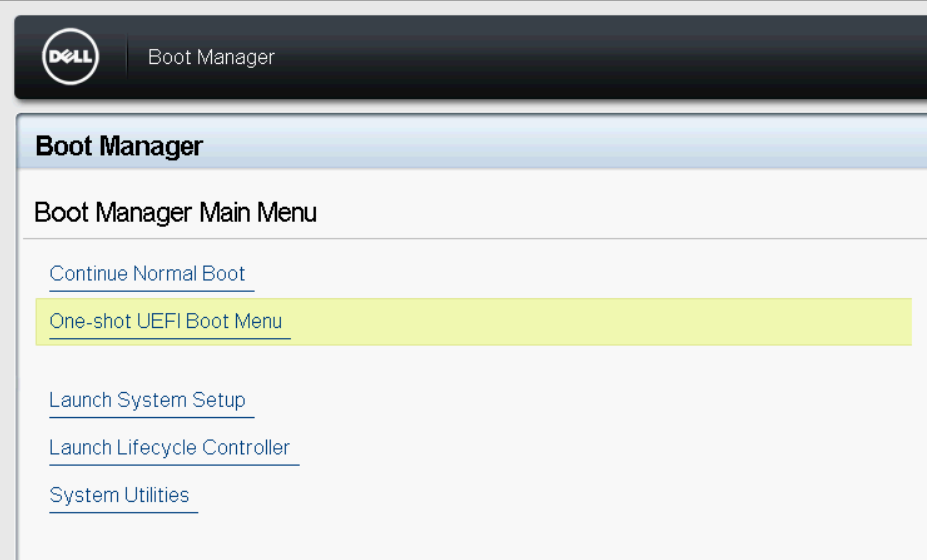
Select Oneshot UEFI Boot option
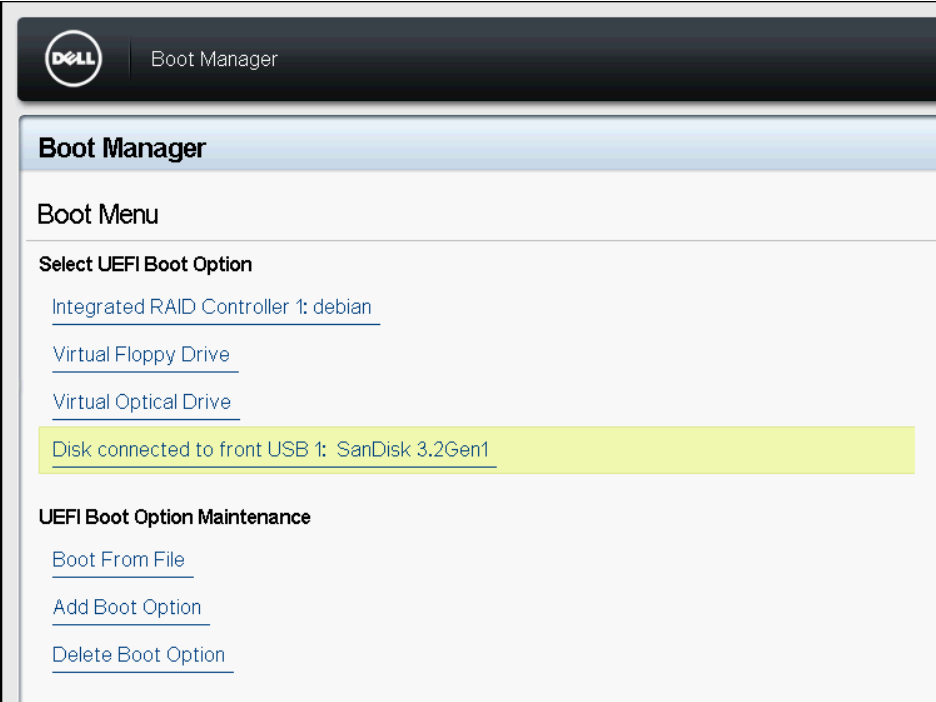
Select boot from the USB stick
Select Install Server
Select English Language (or whatever your choice is)
I preferred to update the installer
Default keyboard layout
Configure static IP for the first interface
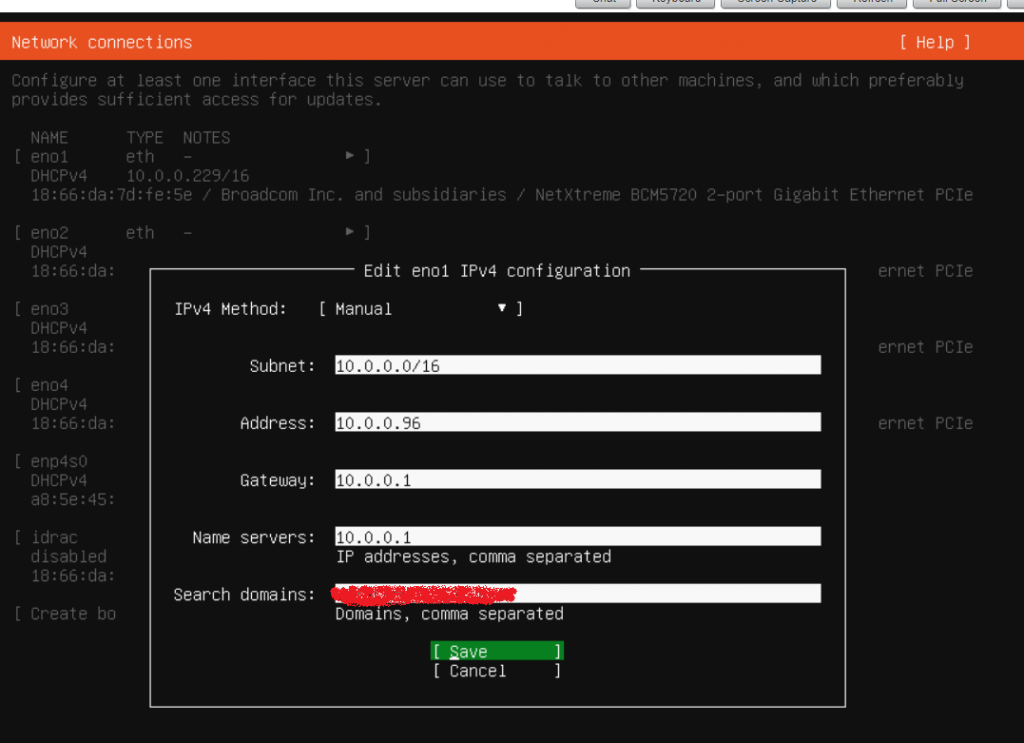
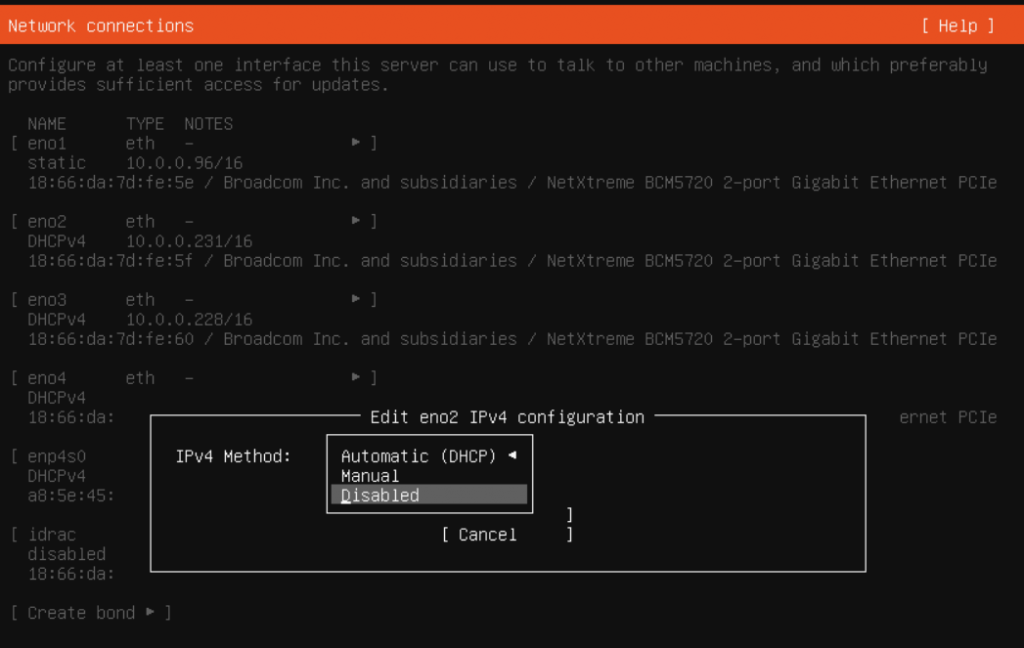
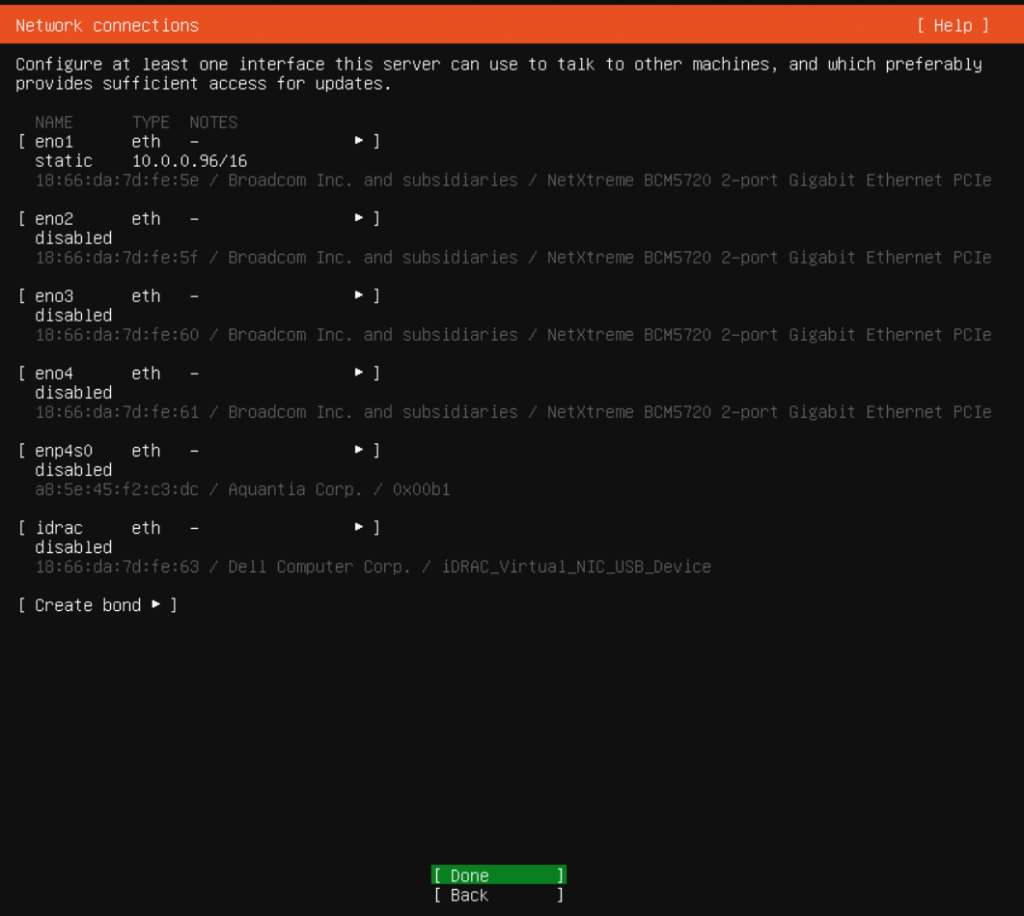
Disable configurations for other interfaces – we will configure after the installation as required.
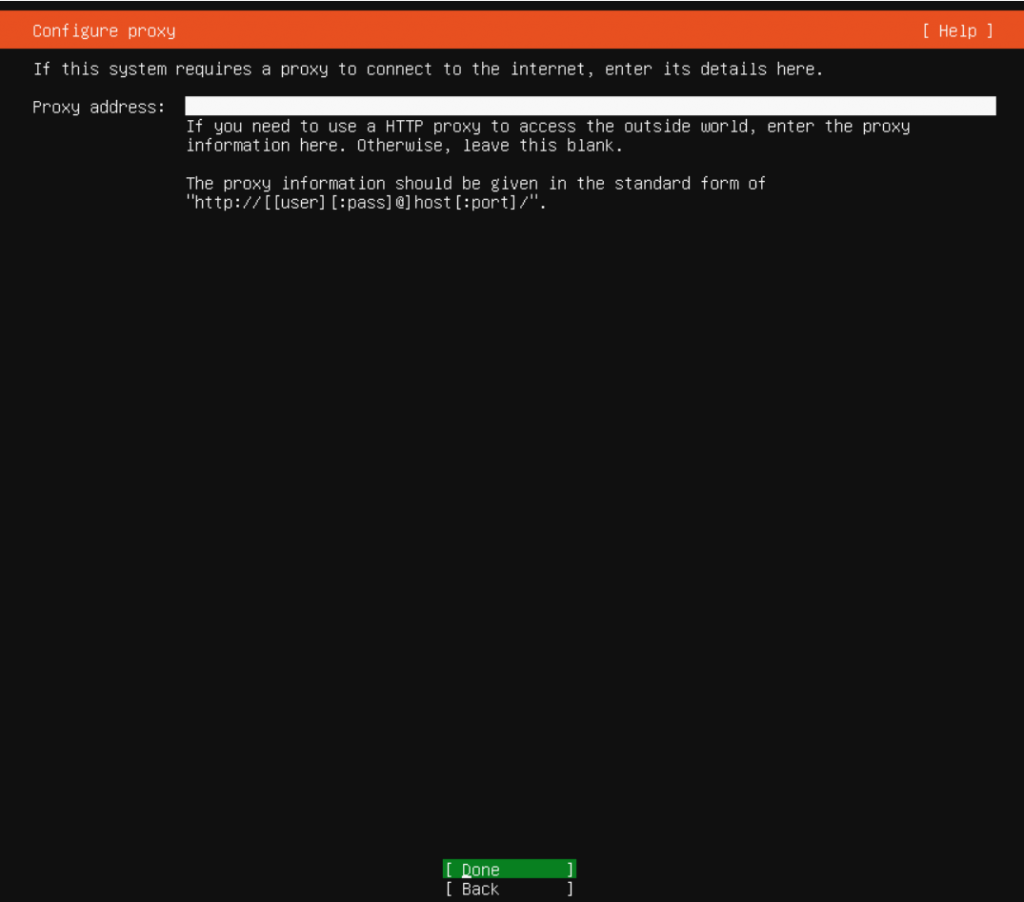
No proxy (in my case)
Default mirror
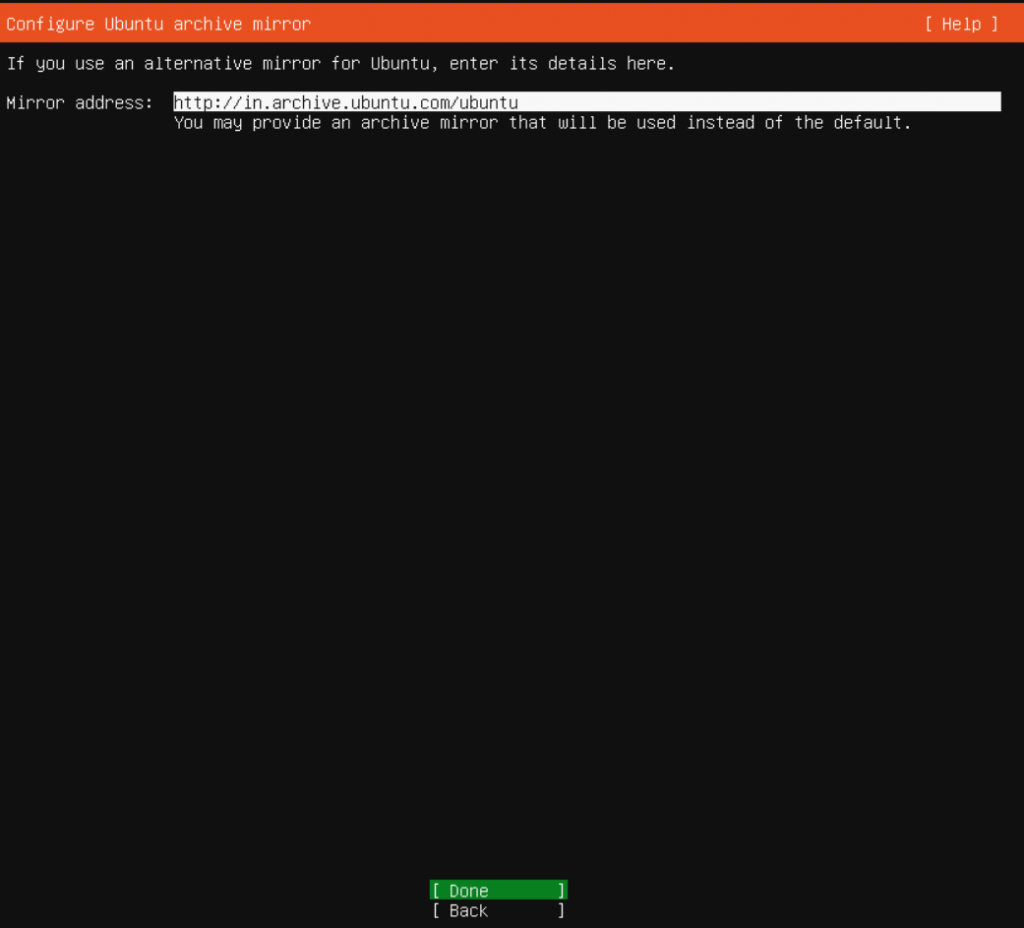
I always prefer custom storage
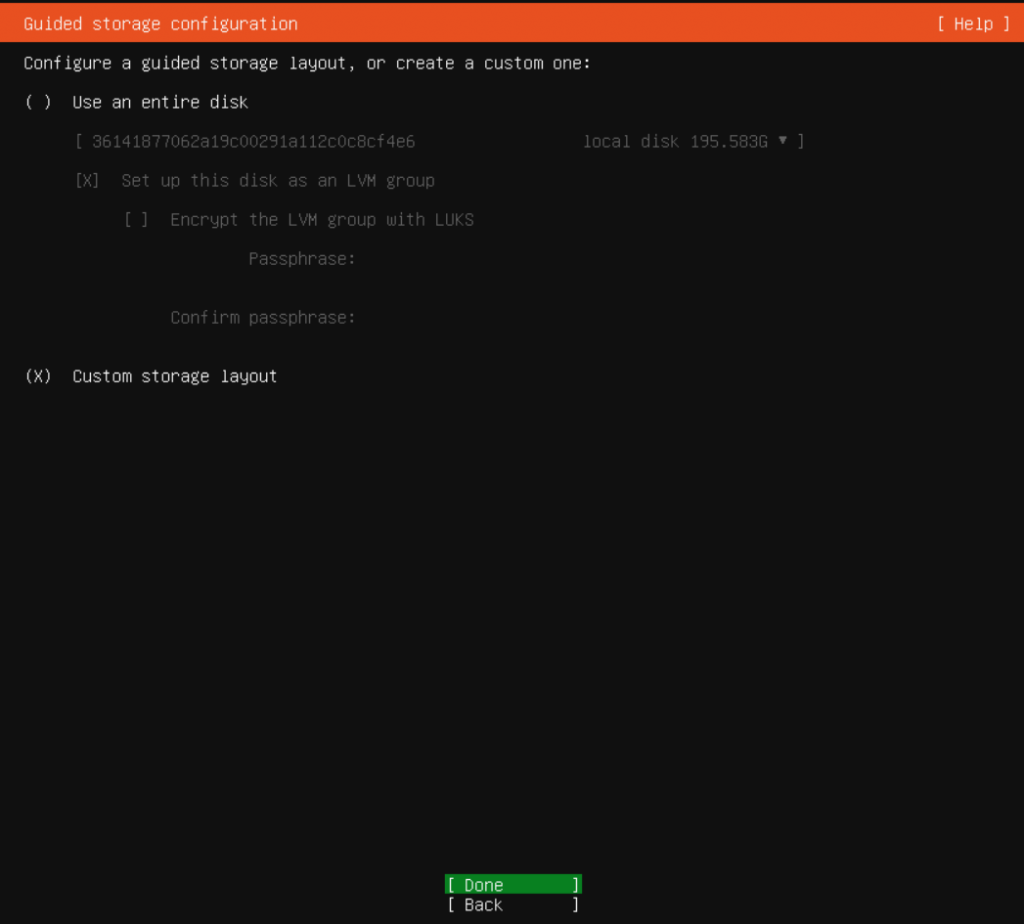
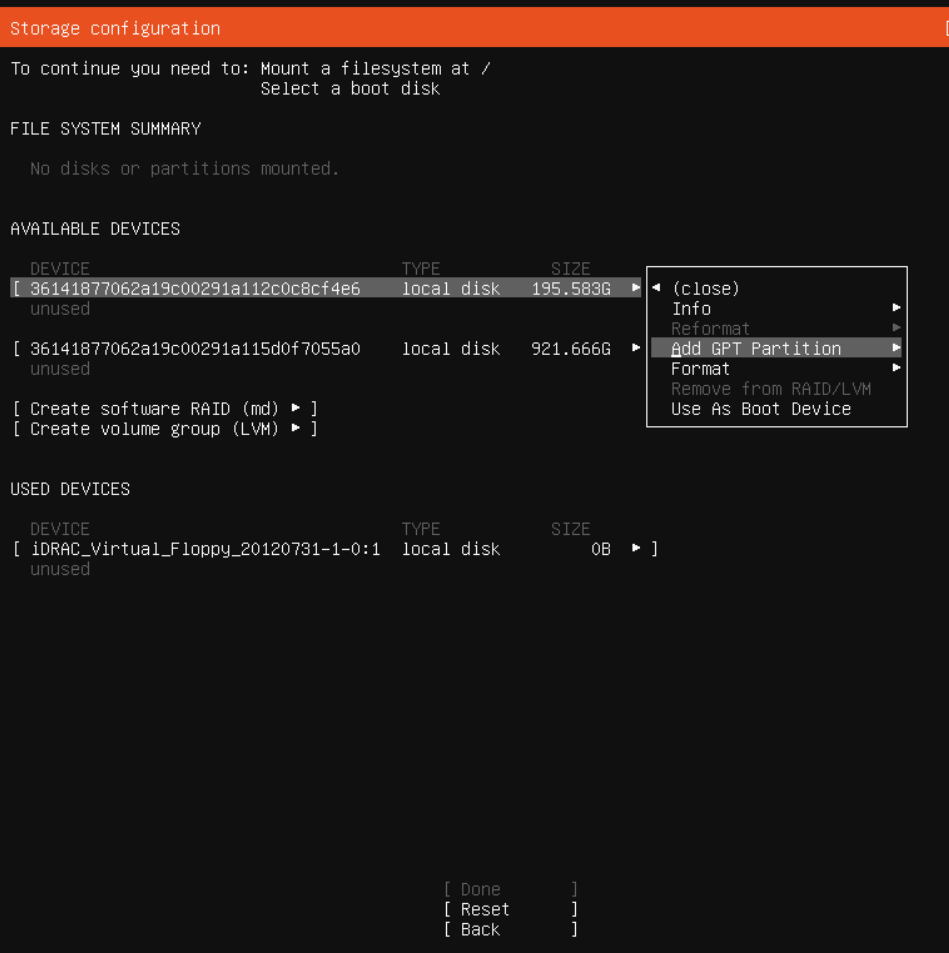
Add GPT Partition
Single partition (my preference)
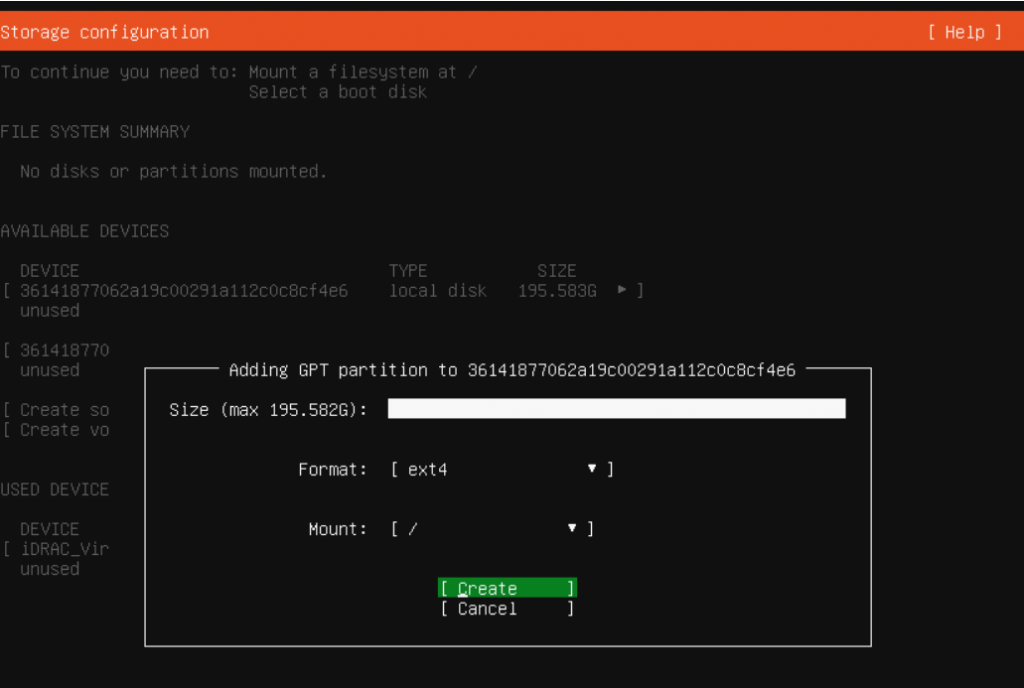
Done with partition configuration
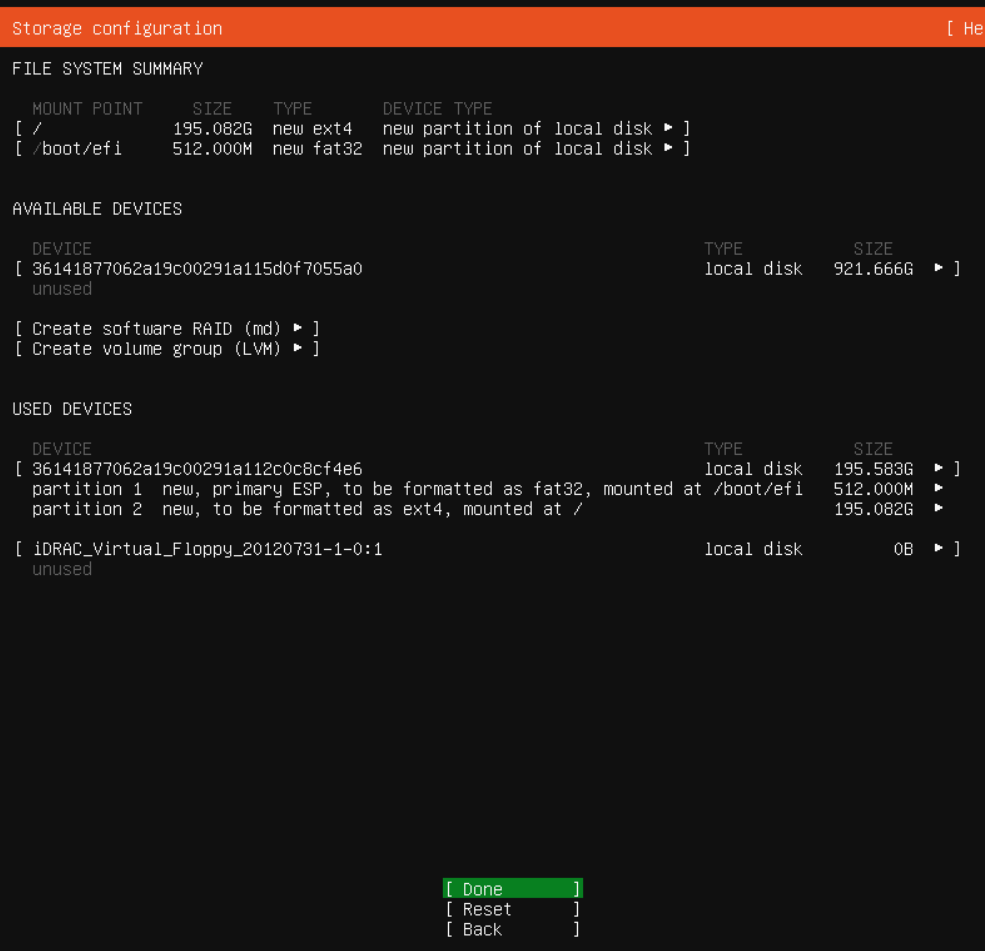
Confirm and continue
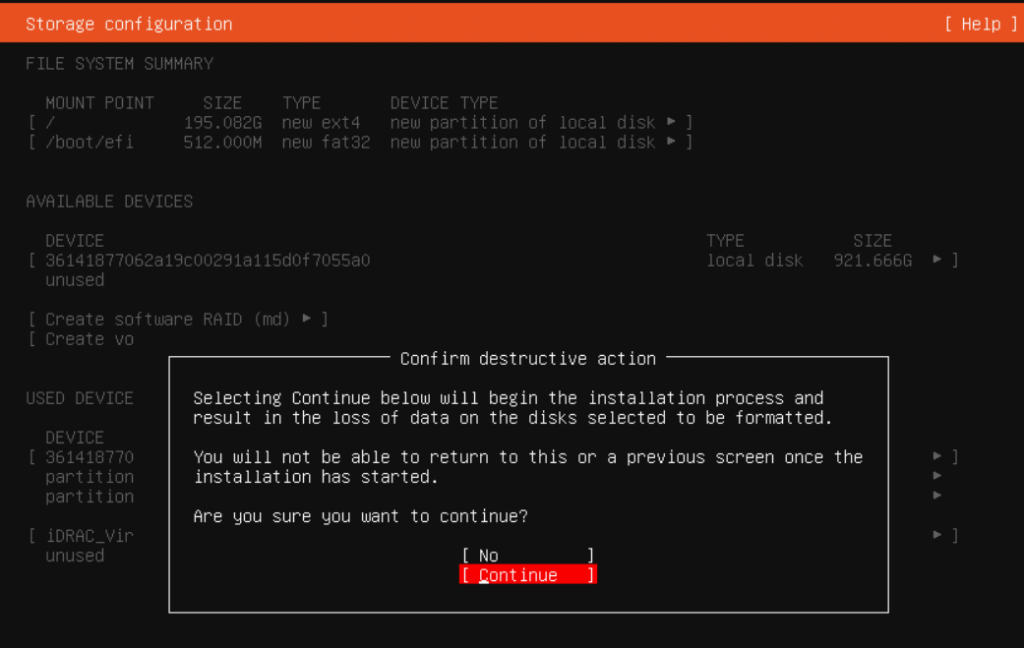
User account setup
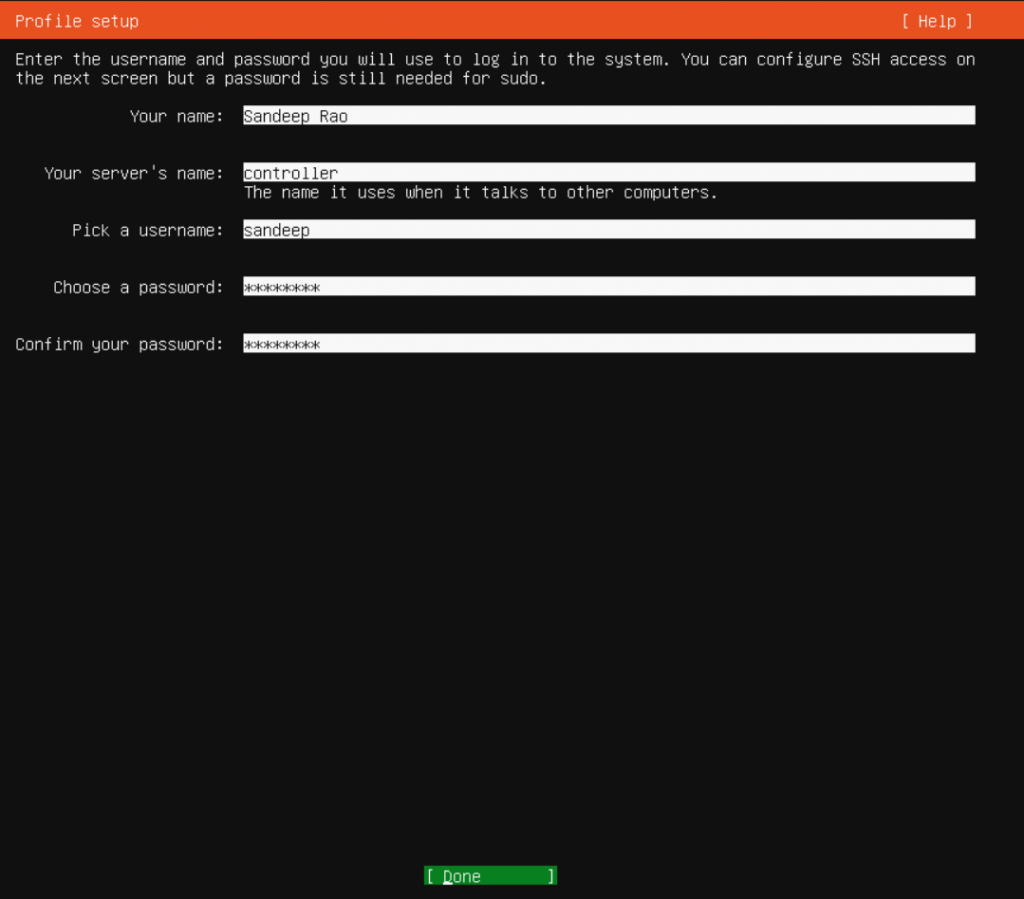
Need ssh access
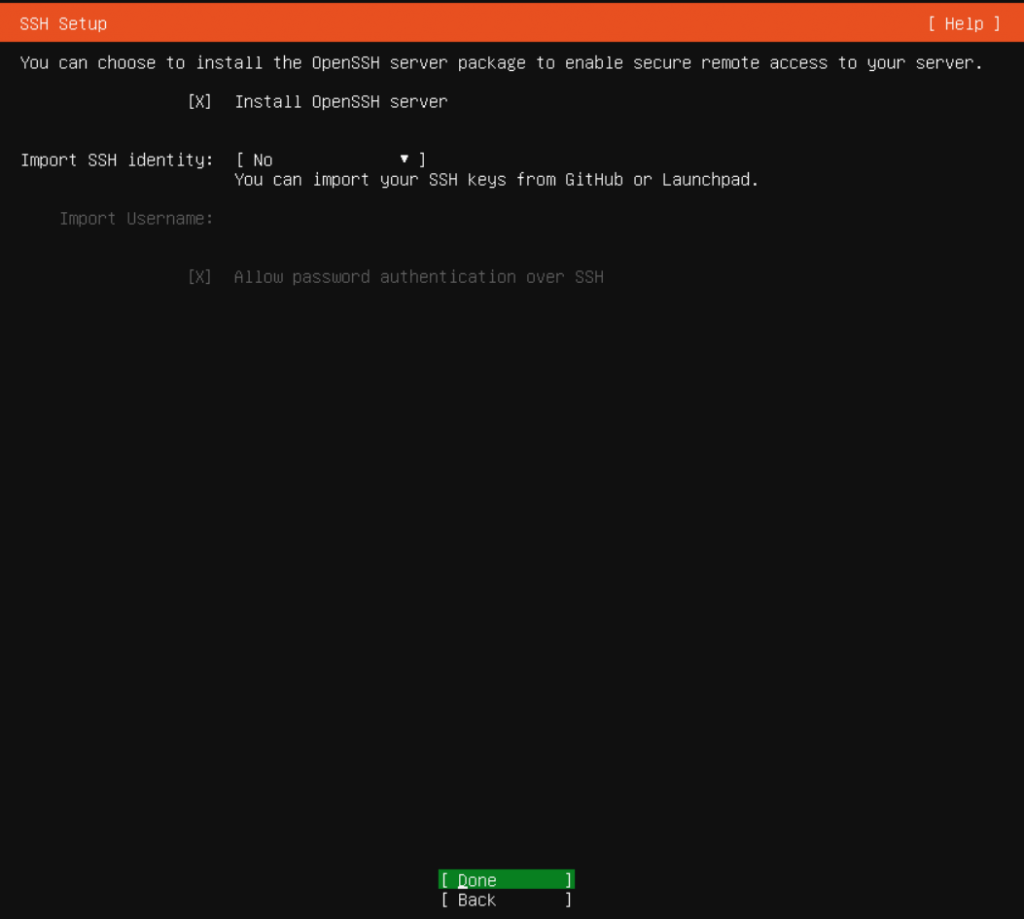
No extra packages
Wait for installation and security updates installation to complete
Installation completed. Reboot.
Login to the server using the user account configured during installation
Is swap enabled and being used? Check the top command output.
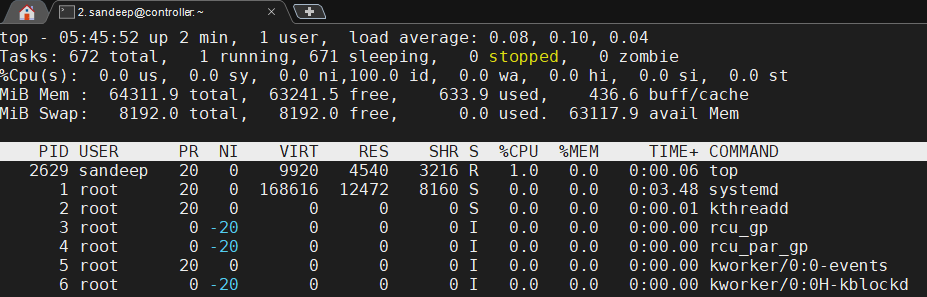
Swap image file present
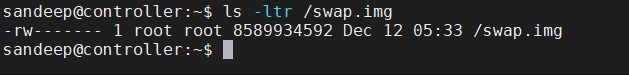
Disable swap, remove swap image file, and reboot.
sudo systemctl stop swap.img.swap sudo systemctl disable swap.img.swap sudo systemctl mask swap.img.swap sudo swapoff -a sudo rm -f /swap.img sudo reboot
Swap disabled
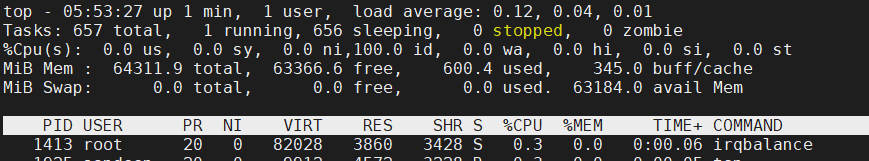
Update repository, upgrade packages and install required packages (mdraid2 to avoid errors in Syslog during startup)
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade -y
sudo apt install -y ifupdown net-tools curl make libblockdev-mdraid2We will be enabling legacy networking. Let us ensure resolv.conf gets updated with required configurations on boot always. Uncomment and update the configurations in /etc/systemd/resolved.conf
# This file is part of systemd.
#
# systemd is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it
# under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by
# the Free Software Foundation; either version 2.1 of the License, or
# (at your option) any later version.
#
# Entries in this file show the compile time defaults.
# You can change settings by editing this file.
# Defaults can be restored by simply deleting this file.
#
# See resolved.conf(5) for details
[Resolve]
DNS=10.0.0.1
FallbackDNS=8.8.8.8
Domains=******
#LLMNR=no
#MulticastDNS=no
#DNSSEC=no
#DNSOverTLS=no
#Cache=no-negative
#DNSStubListener=yes
#ReadEtcHosts=yes
Create a soft link to the systemd generated resolv.conf
sudo ln -sf /run/systemd/resolve/resolv.conf /etc/resolv.conf Update the network configuration – /etc/network/interfaces
Note: Use the ifconfig or ‘ip a’ command to find the interface name. (In my case, it was eno1)
# interfaces(5) file used by ifup(8) and ifdown(8)
# Include files from /etc/network/interfaces.d:
source-directory /etc/network/interfaces.d
auto eno1
iface eno1 inet static
address 10.0.0.96/16
gateway 10.0.0.1
Perform the following from the console – as we will lose connectivity.
Disable systemd-networkd, remove netplan, enable legacy networking
sudo systemctl stop systemd-networkd.socket systemd-networkd networkd-dispatcher.service systemd-networkd-wait-online
sudo systemctl disable systemd-networkd.socket systemd-networkd networkd-dispatcher.service systemd-networkd-wait-online
sudo systemctl mask systemd-networkd.socket systemd-networkd networkd-dispatcher.service systemd-networkd-wait-online
sudo apt -y purge nplan netplan.io
sudo systemctl unmask networking
sudo systemctl enable networking
reboot Set password for the root account
sandeep@controller:~$ sudo passwd
[sudo] password for sandeep:
New password:
Retype new password:
passwd: password updated successfully
sandeep@controller:~$
To enable remote login using the root account, edit /etc/ssh/sshd_config, uncomment and update the following configurations.
#LoginGraceTime 2m
PermitRootLogin yes
#StrictModes yes
#MaxAuthTries 6
#MaxSessions 10
PubkeyAuthentication yes
# Expect .ssh/authorized_keys2 to be disregarded by default in future.
AuthorizedKeysFile .ssh/authorized_keys .ssh/authorized_keys2 We do not want unattended-upgrades – edit /etc/apt/apt.conf.d/20auto-upgrades and update as shown below
APT::Periodic::Update-Package-Lists "0";
APT::Periodic::Unattended-Upgrade "0";Disable services and purge
sudo systemctl disable unattended-upgrades.service
sudo systemctl mask unattended-upgrades.service
sudo systemctl disable apt-daily-upgrade.timer
sudo systemctl mask apt-daily-upgrade.timer
sudo apt remove -y --purge unattended-upgradesRemove snaps and purge snapd (use sudo snap list to get a list of snaps, if remove fails due to dependency resolve the same. Observed while installing on KVM guest core20 was listed) (Disable AppArmor service too)
sudo snap remove lxd
sudo snap remove core18
sudo snap remove snapd
sudo systemctl stop snapd.service snapd.socket snapd.seeded.service apparmor.service snapd.apparmor.service
sudo systemctl disable snapd.service snapd.socket snapd.seeded.service apparmor.service snapd.apparmor.service
sudo systemctl mask snapd.service snapd.socket snapd.seeded.service apparmor.service snapd.apparmor.service
# All other snapd related services
sudo systemctl stop snapd.failure.service snapd.autoimport.service snapd.recovery-chooser-trigger.service snapd.snap-repair.service snapd.system-shutdown.service snapd.core-fixup.service snapd.snap-repair.timer
sudo systemctl disable snapd.failure.service snapd.autoimport.service snapd.recovery-chooser-trigger.service snapd.snap-repair.service snapd.system-shutdown.service snapd.core-fixup.service snapd.snap-repair.timer
sudo systemctl mask snapd.failure.service snapd.autoimport.service snapd.recovery-chooser-trigger.service snapd.snap-repair.service snapd.system-shutdown.service snapd.core-fixup.service snapd.snap-repair.timer
sudo apt purge -y snapd
sudo apt -y autoremoveRemove any stale folders/files.
rm -rf ~/snap
sudo rm -rf /snap
sudo rm -rf /var/snap
sudo rm -rf /var/lib/snapd Disable motd-news (message of the day?) – edit and update configuration in /etc/default/motd-news as shown below.
# Enable/disable the dynamic MOTD news service
# This is a useful way to provide dynamic, informative
# information pertinent to the users and administrators
# of the local system
ENABLED=0
# Configure the source of dynamic MOTD news
# White space separated list of 0 to many news services
# For security reasons, these must be https
# and have a valid certificate
# Canonical runs a service at motd.ubuntu.com, and you
# can easily run one too
URLS="https://motd.ubuntu.com"
# Specify the time in seconds, you're willing to wait for
# dynamic MOTD news
# Note that news messages are fetched in the background by
# a systemd timer, so this should never block boot or login
WAIT=5Disable and mask service
# systemctl disable motd-news.timer
Removed /etc/systemd/system/timers.target.wants/motd-news.timer.
# systemctl mask motd-news.timer
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/motd-news.timer → /dev/null.
Comment configurations in /etc/pam.d/sshd as shown below
# Print the message of the day upon successful login.
# This includes a dynamically generated part from /run/motd.dynamic
# and a static (admin-editable) part from /etc/motd.
#session optional pam_motd.so motd=/run/motd.dynamic
#session optional pam_motd.so noupdate
# Print the status of the user's mailbox upon successful login.
#session optional pam_mail.so standard noenv # [1]
Remove execute permissions motd-news scripts as shown below and restart sshd services
sudo chmod -x /etc/update-motd.d/10-help-text /etc/update-motd.d/50-motd-news
sudo service sshd restartSet the timezone
sandeep@controller:~$ date
Sun 12 Dec 2021 06:44:51 AM UTC
sandeep@controller:~$ sudo timedatectl set-timezone Asia/Kolkata
sandeep@controller:~$ date
Sun 12 Dec 2021 12:15:13 PM ISTIncrease the max number of file descriptors and processes – add the following in /etc/security/limits.conf and reboot.
* hard nofile 65536
* soft nofile 65536
* hard nproc 65536
* soft nproc 65536